Have we measured nucleic acid so many times? Have we ever been “tube long”? For the nucleic acid sample tube in the liquid, do not know the screen in front of you will be curious? What exactly does it do? Why is it red?
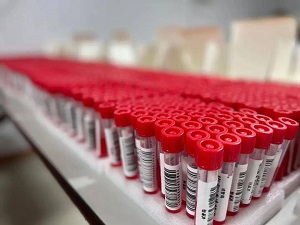
What is the red liquid in the nucleic acid tube?
What does it do?
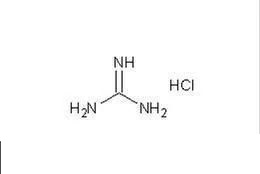
The red liquid in the nucleic acid sample tube is called viral nucleic acid preservation solution.
Guanidine salt is one of the important components of virus nucleic acid storage solution. Guanidine is a strong mono-base, with a basic similar to sodium hydroxide, which can absorb carbon dioxide from the air to form carbonate.
Guanidine is unstable under alkaline conditions, easy to hydrolyze into ammonia and urea and stable under acidic conditions, so it is generally made into guanidine salt for preservation, commonly used guanidine salts are guanidine isothiocyanate or guanidine hydrochloride, etc.
Guanidine is a commonly used protein denaturant, which can destroy the protein coat on the virus’s surface, thereby exposing the nucleic acid under test.
Because guanidine in an aqueous solution will eventually hydrolyze into ammonia and urea, ammonia will be converted into urea under the liver’s metabolism, so guanidine’s toxicity can be equal to urea. The excess urea in our bodies is excreted in urine through our kidneys.
The preservation solution also contains a certain amount of double imidazole alkanes because it has a certain bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect. Usually used as a preservative, we are commonly used in facial masks, emulsions some also added. Low-dose exposure is no risk. In the case of skin, do not worry too much. Clean water can be.
As for the preservative, why is it red? Because of the addition of a reagent called phenol red
Phenol red is an acid-base indicator. It is orange in neutral conditions, turns red when it is basic and yellow when it is acidic.
If the storage solution is contaminated with bacteria (usually when the storage solution fails or bacteria are present in the sample), the liquid’s PH drops, turning from red to yellow.
In addition, the inorganic salts in nucleic acid storage solution can maintain a relatively stable PH value; The nutrients in it will ensure that the viral nucleic acid will not be cleaved for a short time.
Here we can clear “red water water” the main role is to inactivate the virus bactericidal inhibition and ensure the stability of nucleic acid.
In short, the ultimate purpose of nucleic acid preservation solution is to make the nucleic acid in the test sample properly preserved and detect the virus in time.
In addition, the red colour of nucleic acid detection liquid is intentional to have a striking reminder and distinction. If it’s a clear, colourless liquid, that’s fine, but red is more eye-catching.
And what if someone accidentally poured a nucleic acid test that looks like raspberry juice into their mouth?
If you accidentally eat it, you should go to a professional medical institution in time because the ingredients in the nucleic acid test solution are buffer solution and some chemical components. If you find that you have eaten it by mistake, you must go to the hospital immediately.
How to guarantee the transportation safety of nucleic acid tubes be?
Where does it end up?
Upon completion of sampling, the nucleic acid sample storage tube will be immediately placed into a Ziploc bag, a yellow medical bag, and a dedicated biosafety transport box.
The box is equipped with an ice pack to keep the sample at a low temperature of 4 degrees Celsius because the lower the temperature, the more stable the nucleic acid. With “low-temperature protection” and “nucleic acid preservation solution”, these two “double insurance” can very well guarantee the accuracy of laboratory detection results.
For the transport time, according to the unified national standards, in principle, samples should be collected every 2 hours for transport, and the samples should be sent to the laboratory for testing within 3 hours after collection.
After the completion of nucleic acid detection, the nucleic acid is sealed, disinfected, and sent to the terminal treatment plant by special personnel and special vehicles. The transportation is safe and pollution-free.
Generally, the tubes or specimens of negative nucleic acid storage solution shall be cleared and processed by professional companies by medical waste disposal standards. Positive specimens must be autoclaved and treated according to general medical waste.
Post time: Oct-19-2022